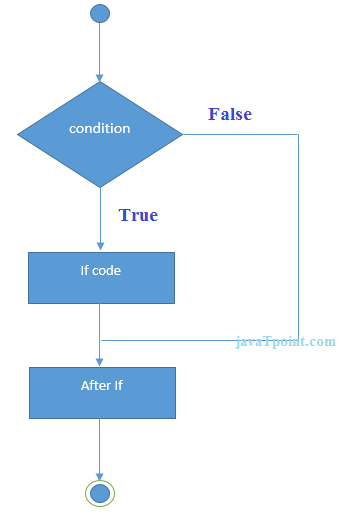
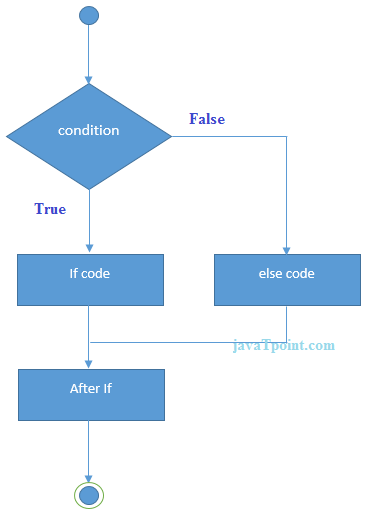
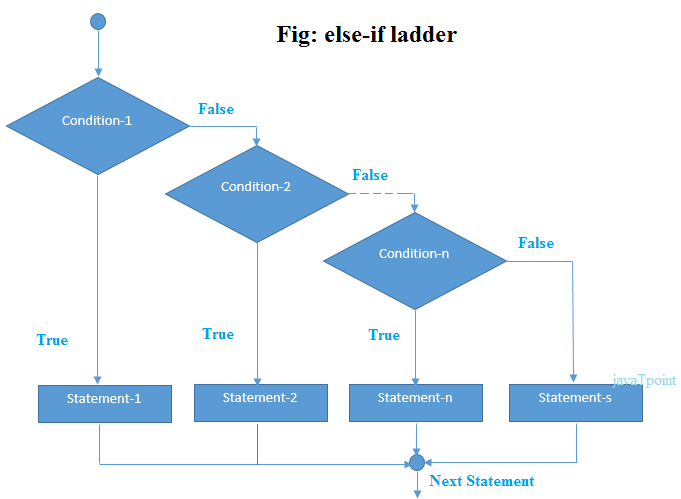
In C++ programming, if statement is used to test the condition. There are various types of if statements in C++.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- nested if statement
- if-else-if ladder
The C++ if statement tests the condition. It is executed if condition is true.
if(condition){
//code to be executed
} #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int num = 10;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
cout<<"It is even number";
}
return 0;
} Output
It is even number
The C++ if-else statement also tests the condition. It executes if block if condition is true otherwise else block is executed.
if(condition){
//code if condition is true
}else{
//code if condition is false
} #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int num = 11;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
cout<<"It is even number";
}
else
{
cout<<"It is odd number";
}
return 0;
} Output
It is odd number
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int num;
cout<<"Enter a Number: ";
cin>>num;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
cout<<"It is even number"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"It is odd number"<<endl;
}
return 0;
} Output
Enter a number:11
It is odd number
Enter a number:12
It is even number
Syntax
if(condition1){
//code to be executed if condition1 is true
}else if(condition2){
//code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
else if(condition3){
//code to be executed if condition3 is true
}
...
else{
//code to be executed if all the conditions are false
} #include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
int num;
cout<<"Enter a number to check grade:";
cin>>num;
if (num <0 || num >100)
{
cout<<"wrong number";
}
else if(num >= 0 && num < 50){
cout<<"Fail";
}
else if (num >= 50 && num < 60)
{
cout<<"D Grade";
}
else if (num >= 60 && num < 70)
{
cout<<"C Grade";
}
else if (num >= 70 && num < 80)
{
cout<<"B Grade";
}
else if (num >= 80 && num < 90)
{
cout<<"A Grade";
}
else if (num >= 90 && num <= 100)
{
cout<<"A+ Grade";
}
} Output
Enter a number to check grade:66
C Grade